

Underlying biomechanical discrepancies such as a hyperpronated foot can further contribute to the development of lower limb pain as a result of abnormalities in movement postural anomalies force the lower extremity to adapt by compensating for the lack of proper foundational support from the feet.Īs part of a comprehensive rehabilitative strategy for compartment syndrome coupled with a foot posture abnormality, MASS4D® foot orthotics act as pain-management devices to decrease any additional stress on the affected limbs by reinforcing the optimal movement of the lower extremity and preventing the chances of recurrences or injury.Ĭopyright 2017 MASS4D® All rights reserved. This can be beneficial in minimising excessive pressure in the lower limbs while promoting normal ambulation during recovery. The authors also suggest modifications in footwear and wearing foot orthotics to gradually assist the patient in returning to their former level of functionality. This can be in conjunction with ice therapy and the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. recommend the first line of treatment as lessening the intensity and frequency of activity. While discussing the conservative management of two patients with bilateral soleus syndrome or chronic exertional compartment syndrome of the superficial posterior compartment, Gross et al. This is necessary since during exertion, compartment pressures in patients with the condition increase drastically and take longer to return to their baseline. In addition, none of these studies directly compared endoscopic with open or mini-open groups.
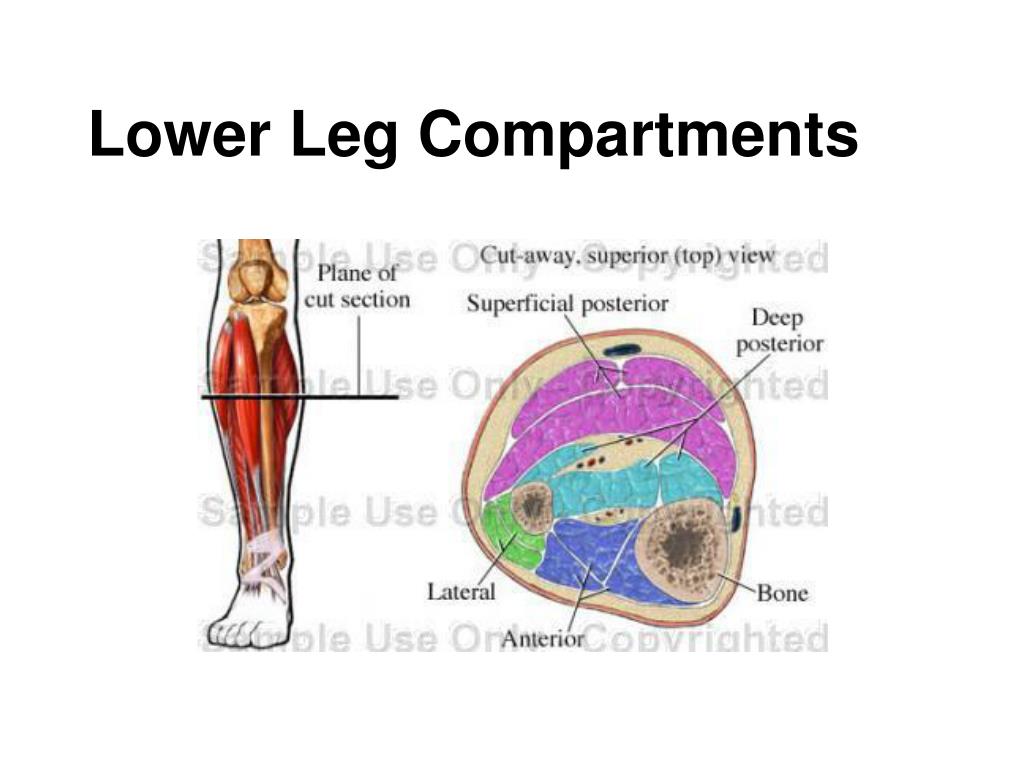
The authors described an increase of up to 20 percent in muscle volume and weight during strenuous exercise and a reduction in reserve volume within fascial compartment due to the normal muscular hypertrophy that occurs over time with chronic exercise.ĭiagnosing chronic compartment syndrome can be challenging and requires invasive intra-compartmental pressure monitoring both pre- and post-exertion. Outcomes of endoscopic release of lower-extremity compartments for CECS have only been reported in 3 previous studies 5, 14, 16 and have been limited by small sample size. In a comprehensive study conducted on 123 patients with extremity muscle pain, swelling and paraesthesia, Islam and Robbs observed that the most commonly affected lower limb muscle groups were the anterolateral, deep posterior and superficial posterior compartments. It is considered to be the most common cause of exercise-induced leg pain. It is important to note here that there may be an absence of pain in the later stages of the condition.Ĭhronic compartment syndrome is an overuse injury of the lower extremity that causes a dull aching pain which intensifies with exertion in sports such as running or football. Anterior tibial compartment syndrome Anterior tibial syndrome Nontraumatic compartment syndrome of leg Nontraumatic compartment syndrome of lower extremity. Action: Extension of the great toe and dorsiflexion of the foot.The clinical presentation of acute compartment syndrome includes pain, paresthesia, pallor, paralysis and raised intra-compartment pressure.Each compartment has a covering of fascia. The tendon crosses anterior to the ankle joint and attaches to the base of the distal phalanx of the great toe. There are four compartments in the lower leg one in the front, one on the outside, and two in the back (superficial and deep). Attachments: Originates from the medial surface of the fibular shaft.Its tendon emerges from between the two muscles to insert onto the big toe. The extensor hallucis longus is positioned deep to tibialis anterior and extensor digitorum longus. Actions: Extension of the lateral four toes, and dorsiflexion of the foot.The tendon splits into four and each tendon inserts onto a toe.The fibres converge into a tendon, which travels onto the dorsal surface of the foot.Originates from the lateral condyle of the tibia and the medial surface of the fibula.Its four tendons can be palpated on the dorsal surface of the foot. The saphenous compartment 23 is bounded superficially by a hyperechoic saphenous fascia and rests on the muscular fascia (the Egyptian eye seen on duplex imaging Fig. In the legs, a subcomponent, the saphenous system, is present. The extensor digitorum longus lies laterally and deep to the tibialis anterior. Chronic compartment syndrome is an overuse injury of the lower extremity that causes a dull aching pain which intensifies with exertion in sports such as. The superficial veins are located above the muscular fascia.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
